Our body is an immensely complex system, where different organs and processes can affect each other. It is not unusual to have a long-lasting health issue with no apparent reason. Sometimes all we have to do is to take a look inside the mouth, because the culprit is an innocent looking tooth. This is a casebook example of a focal infection.
Nowadays we hear more and more about focal infection theory, and focal infections. However, not many people fully understand what these terms mean. Focal infection is a process where a chronic infection causes health issues at a different point of the body. This is the focal infection, which can be completely asymptomatic, therefore invisible. However, bacteria will slowly spread from the infection, and enter the bloodstream. Then, they will cause serious trouble on other points of the body.
Symptoms of a focal infection
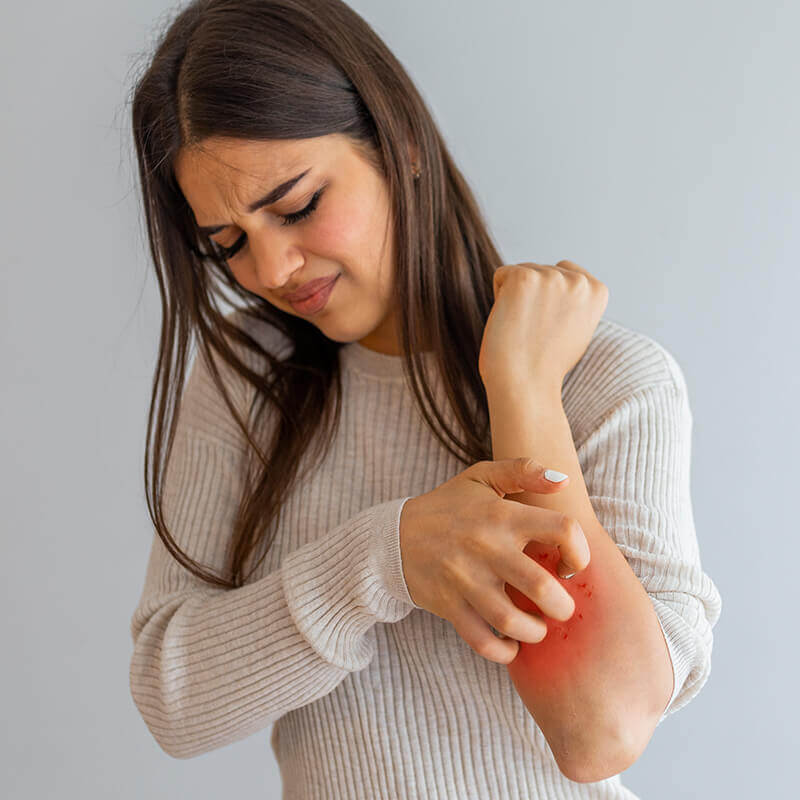
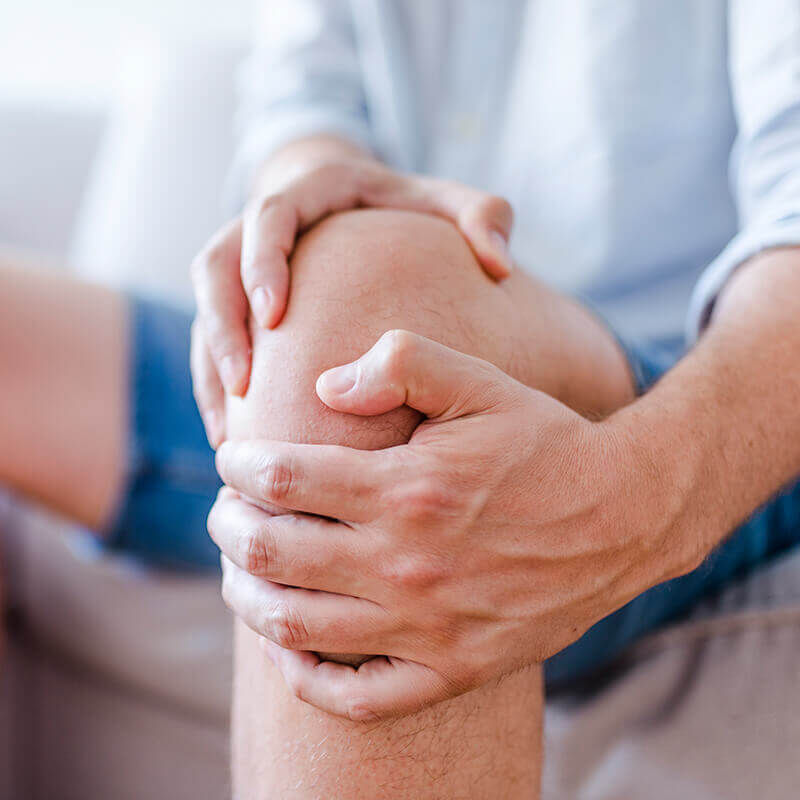
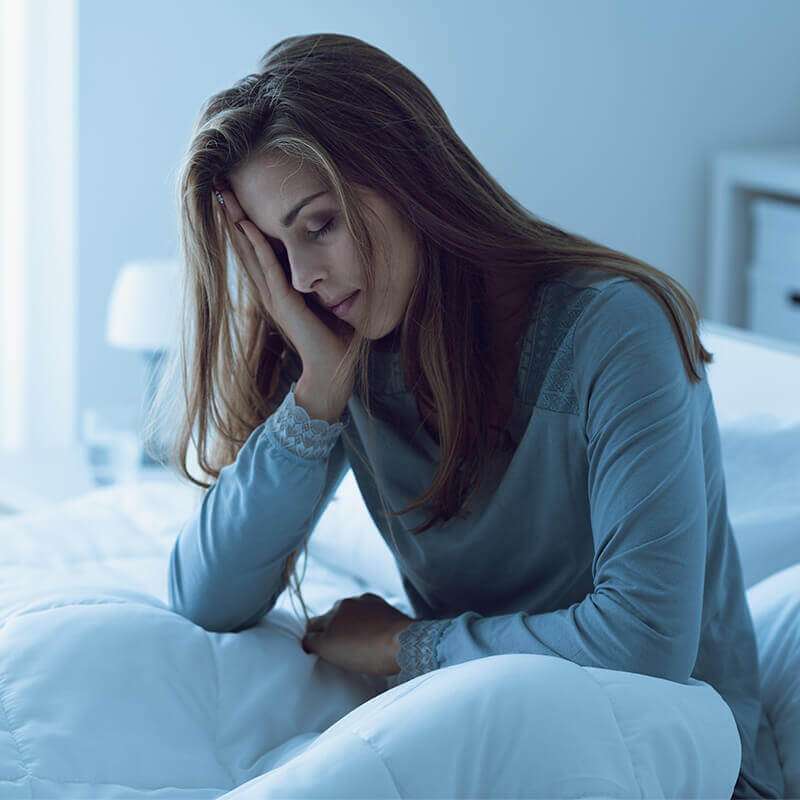
Skin disorders (rashes, acne, and eczema) that won’t go away, or re-appear every now and then, are usually telltale signs of focal infections. Other suspicious problems could be: chronic arthritis, kidney-, colon-, eye-, endocardial infections, hair loss, genital diseases. Furthermore, even unexplainable fatigue, chloraemia, or sleeping disorders can indicate an underlying focal infection.
Prime suspect: the dental focal infection
Focal infection cannot be treated until the source; the nodule is found and terminated. There is a specific diagnosis for this. However, thanks to recent medical studies we already know that nodules appear mainly in the teeth, tonsils, sinuses, gall bladders, and urogenital systems. Therefore, if our general practitioner recommends a search for localized infection, we ought to look for a well-equipped dentistry. First, the dentist will check the vitality of our teeth, then do an examination and take an X-ray. This thorough investigation is necessary because several things can cause the development of a dental nodule.
– decayed tooth
– gum infection
– non-vital tooth, that hasn’t been root canal treated
– improperly carried out root canal treatment
– broken root left in the gum
– broken tooth
– periodontal disease
– tooth unable to surface (e.g. a wisdom tooth)
So what happens after we found the infection?
Once the dentist finds the dental nodule, their primary goal is to remove it while saving the tooth. If this is not possible, the tooth may be extracted, and replaced.
However, just like with almost every health issue, prevention is easier than treatment. Healthy diet, proper dental hygiene, and regular dental checkups are the best way of prevention. Keep these in mind, and your mouth and body will be grateful.


